Cannabis & Me
Cannabis 101
The Endocannabinoid System(ECS):
The Endocannabinoid System of your body is a network of receptors that help to regulate homeostasis or balance by interacting with and supporting a variety of major bodily functions.
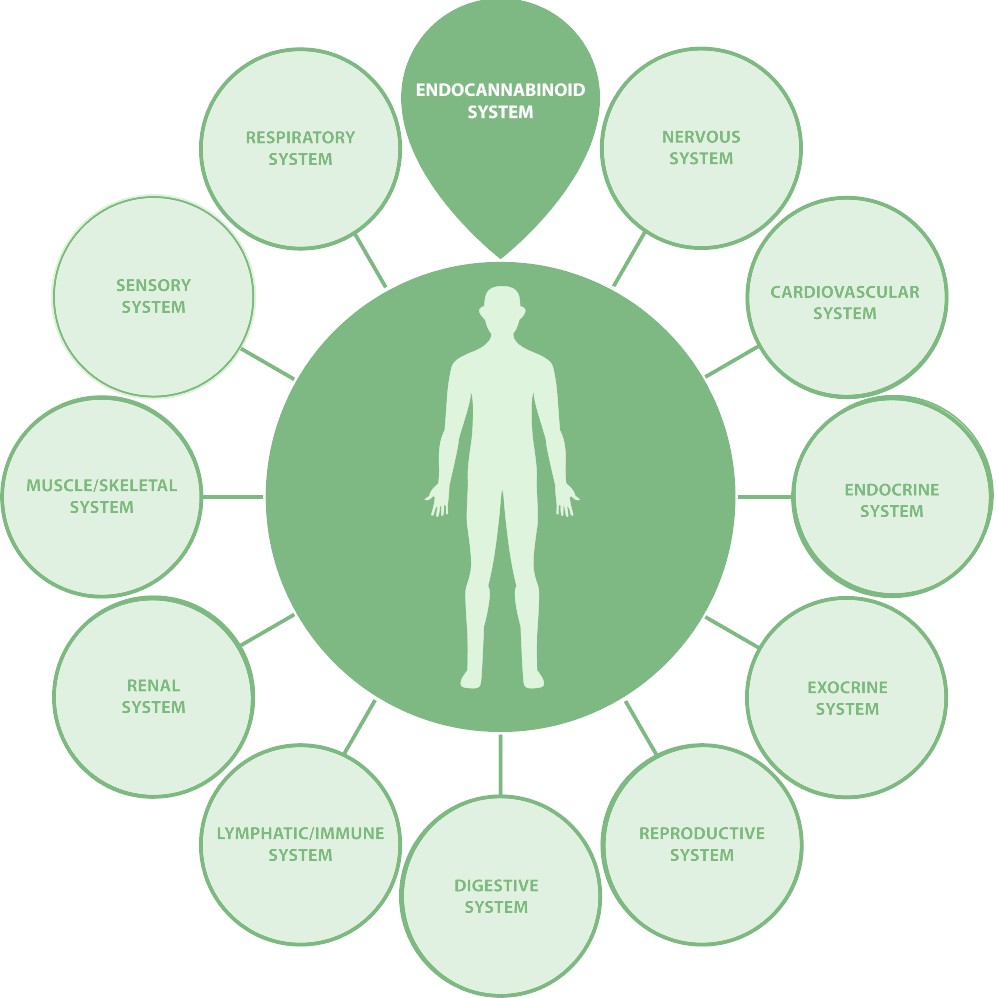
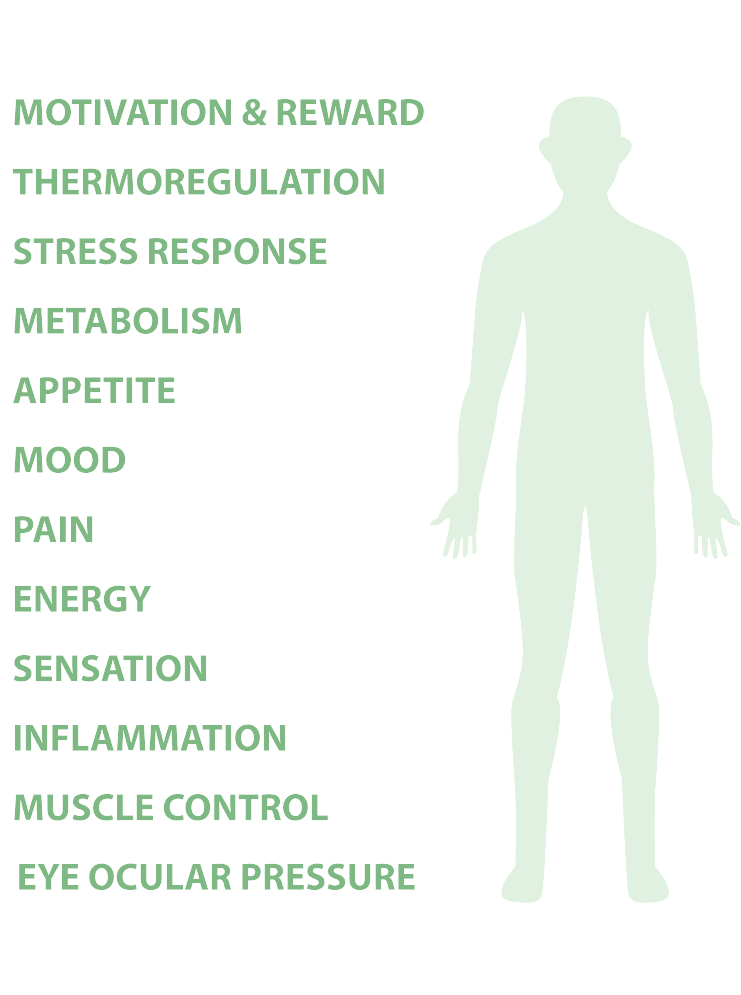
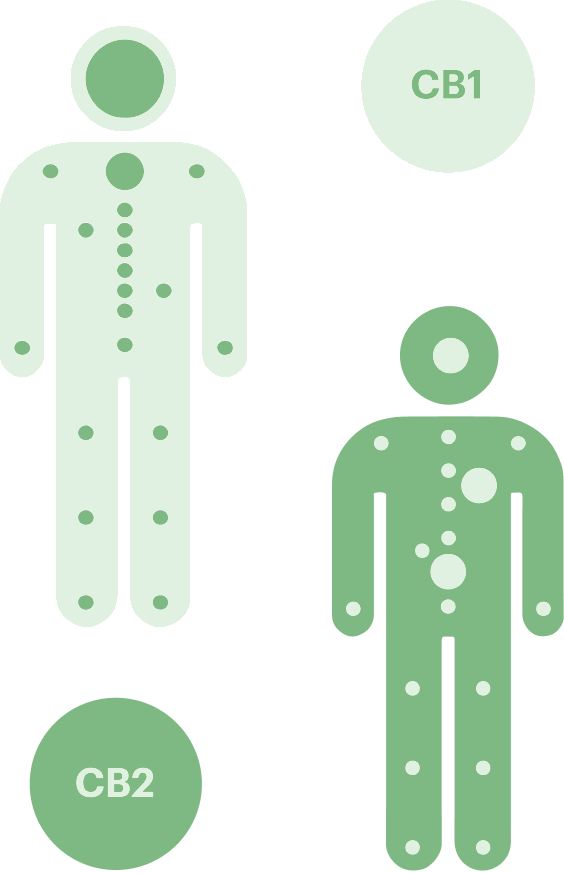
The ECS Receptors
The two main receptors of the endocannabinoid system are known as CB1 CB2 receptors.
CB1 Receptors
CB1 receptors are found primarily throughout the brain and central nervous system. CB1 receptors are also found within the kidneys, liver, lungs, digestive tract and even our eyes.
CB2 Receptors
CB2 receptors are found primarily throughout the immune system. CB2 receptors are also found within our peripheral tissues that exist in our stomach, muscles, glands and even our ears.
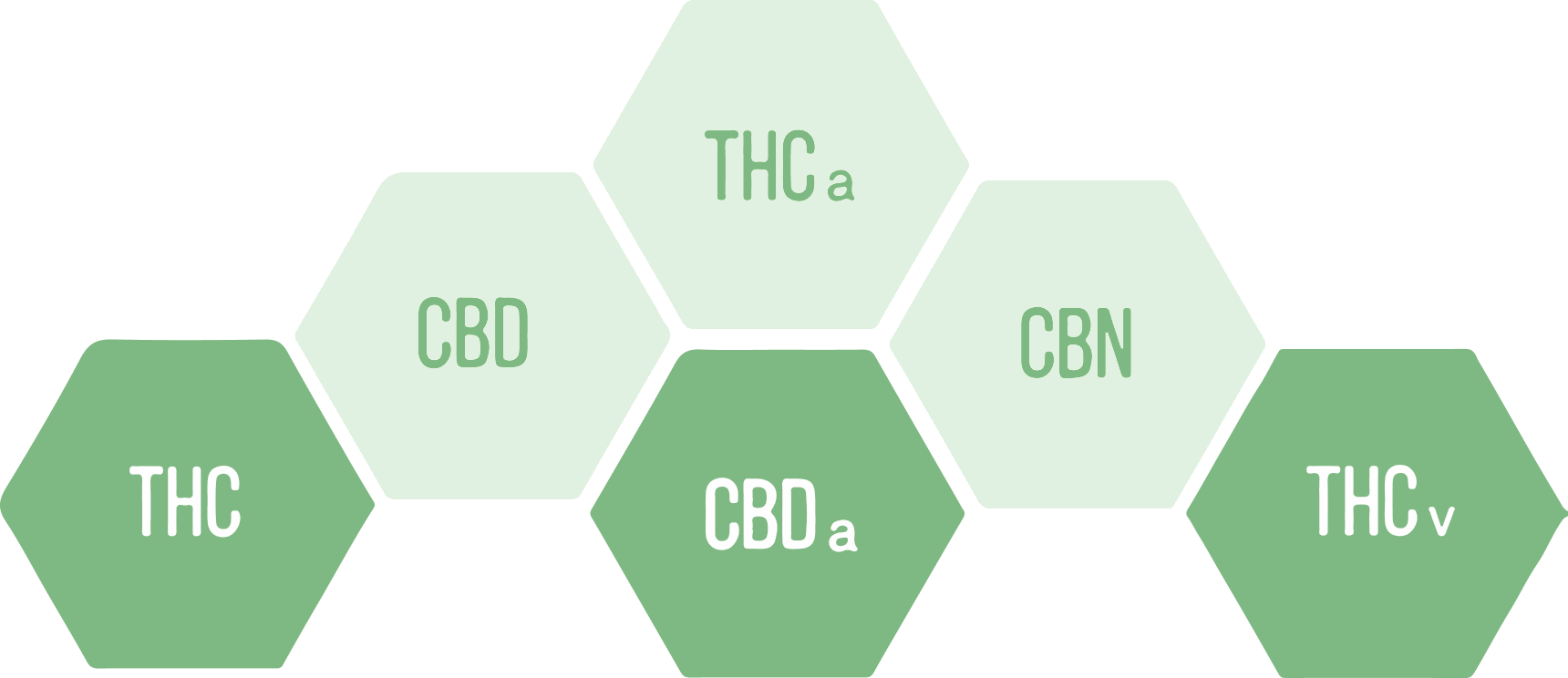
Cannabinoids
Cannabinoids are chemical compounds secreted by the cannabis plant’s trichomes during its growth process. THC & CBD are the most well-known cannabinoids, but there are many others, such as: CBN, CBG, THCA, and THCV.
Cannabinoids work by bonding with the receptors of the ECS and either support what the receptors intended function is or supplement to help change or modulate a receptor’s function(s) if the ECS is out of balance.
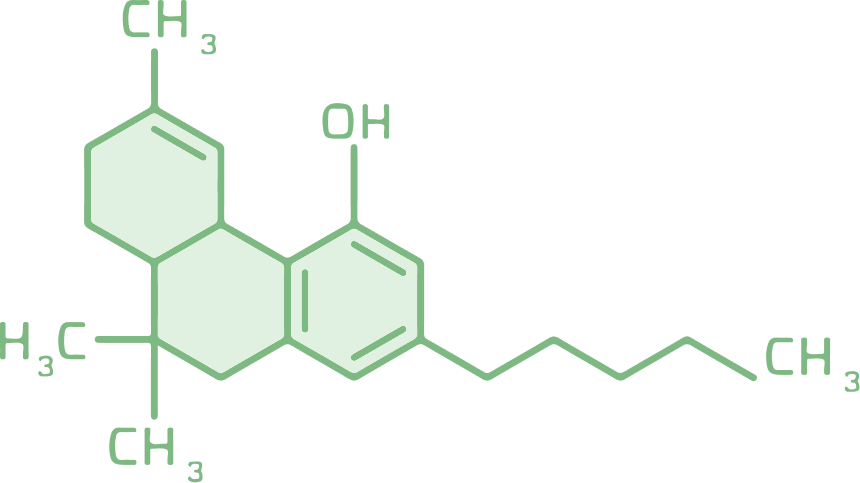
THC
THC, short for tetrahydrocannabinol, is the most well-known cannabinoid. THC is the primary psychoactive component of the marijuana plant and has many potential health benefits.
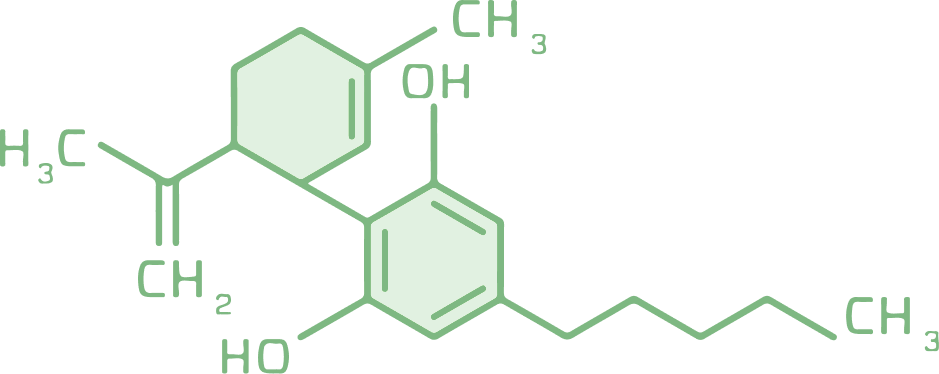
CBD
CBD, short for cannabidiol, is the second most well-known cannabinoid. CBD is known to have many potential health benefits and may mitigate the psychoactive effects of THC.
Cannabis Plant Anatomy
Gender
Female & Sinsemilla
Male
Male cannabis plants produce pollen sacks that blossom into flowers when they reach maturity. They are not as potent as female plants, but do contain cannabinoids. Pollen fertilizes the bud of a female plant and contains genetic material used to breed new strains of marijuana with specific traits over time. Pollinating a female plant creates seeds with genetic material from both the mother and father plant, leading to more genetic variation and a stronger cannabis species (clones of female plants are prone to genetic weakness over time).
Hermaphrodite
A hermaphrodite is a plant that develops both female and male parts. This usually occurs when females have gone a long time without pollination or experience stress during growth.
Visual Components of Cannabis Plant

Trichomes
Trichomes are tiny glands on leaves and calyxes that produce cannabinoids and terpenes. They have a crystal-like appearance and hold the majority of resin. Trichomes and their resin are used to create a variety of concentrates and extracts.

Stigma & Pistil
Pistils contain the reproductive parts of the flower. Stigmas are the vibrant, hair-like strands of the pistil that collect pollen from males. They are only found on female plants and capture pollen from male plants by curling or bending toward male plants. Pistils are a grower’s best tool for differentiating between a male and female plant.

Calyx
The calyx is a tiny, teardrop-shaped cluster that makes up the bud itself. It contains sugar leaves and pistils and is where most of the trichomes are found.

Bract
A bract is a tear-shaped green leaf covered in resin glands. Bracts produce lots of concentrated cannabinoids. They encapsulate the reproductive parts of the female and house seeds in a fertilized plant.

Cola

Sugar Leaves

Fan Leaves

Node
Leaf nodes are where branching occurs off of the stem and where flowers grow. Nodes connect new stem branches that separate and take the form of a leaf, branch, or bud. Internode space is the distance between sets of branches; indicas have shorter internode spacing than sativas.

Stem
Note: Individual results may vary.